A simple comparison scheme
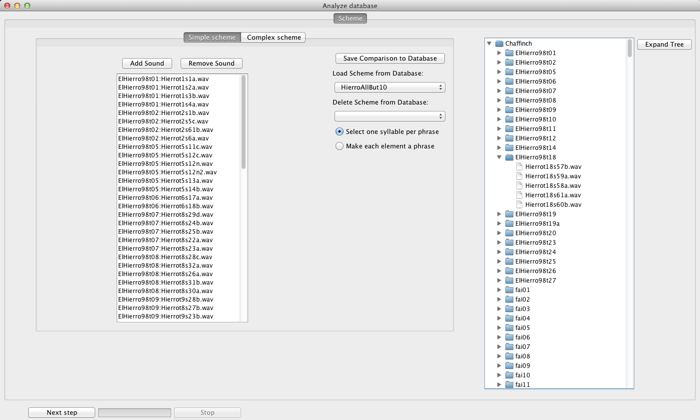
When you first select Analysis from the Database window the window above appears. Its purpose is to allow you to select the sounds you wish to analyze.
On the right-hand side of the window is a panel containing a view of the database you are logged-in to. This is very much the same as the view found in the Database window: it displays individuals, and hierarchically arranged under them, the sounds that have been recorded form them. You can expand and collapse the tree using the Expand Tree button to the right of the panel. Analyses are started by selecting sounds from this view.
On the left-hand side of the window is a different panel, initially containing an empty list. This is a view of Luscinia's "comparison schemes". A simple comparison scheme is one list of sounds, and the scheme tells Luscinia to compare every member of the list with every other member.
To add a sound to a simple scheme, first select it in the database. Then click Add Sound. You can add multiple sounds simultaneously by using the SHIFT or CONTROL/APPLE keys to select multiple items from the database.
To remove a sound from a simple scheme, select it in the scheme list, and click Remove Sound. Again, multiple items can be selected and removed.
When you have created a scheme, click Save Comparison to Database to save the scheme. This creates a record of what you compared, and allows you to repeat the same analysis at a later point in time.
To load a saved comparison from the database, use the drop-down list under Load Scheme From Database. To remove a saved comparison scheme from the database, use Delete Scheme From Database.
The two radio buttons, Select One Syllable Per Phrase and Make Each Element A Phrase provide two shortcuts for analyzing hierarchically structured signals in special ways. Select One Syllable Per Phrase means that one exemplar syllable (from the middle of the phrase) is selected for further analysis. For large databases, in which phrases consist of syllables repeated many times, this option can greatly reduce the processing time for, in particular, Dynamic Time Warping. Make Each Element A Phrase ignores all hierarchical organization of elements into syllables or phrases, and instead makes each element a separate phrase. This changes how distances between songs are later calculated (for example).